GCON: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Hypothesis #2: Gativus Hypothesis on Consciousness, Mind, and Thought== | ||
Gativus hypothesizes that '''Consciousness, Mind, and Thought''' are grounded in a '''cognitive/knowledge network (GCON)'''. This network is composed of: | |||
The | # '''Knowledge Entities (KLEN)''', and | ||
# '''Specific relations''' interconnecting these KLENs. | |||
=== | |||
Gativus | === Definition and Inspiration for KLEN === | ||
The concept of '''KLEN''' is inspired by the '''Resource Description Framework (RDF)''' but extends it significantly to incorporate: | |||
* '''Behavioural activity''' capabilities, and | |||
* Support for '''multiple subjects and objects''' in its structure. | |||
To describe the behavioral nature of KLENs effectively, '''UML activity diagrams''' and '''BPMN notation''' are considered the most mature and widely accepted tools. These notations align with the knowledge base of the majority of computer specialists and provide robust methodologies for modelling dynamic behaviours. | |||
=== KLEN Construction and Representation === | |||
KLENs are constructed using the '''Gativus Network Notation (GNOT)'''. Their design maintains associations with: | |||
* '''RDF principles''', and | |||
* '''UML class and activity diagrams'''. | |||
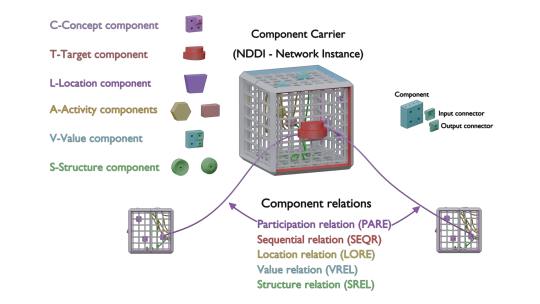
A detailed representation of KLEN construction within GNOT, including these associations, is illustrated below. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines" widths="540" heights="480" perrow="2"> | |||
File:Base animation.mp4 | |||
File:G-NOT with shadow.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[GTOM |'''Axiom #1''': The Human Brain and Multiple Networks]] | |||
* [[OMAP|'''Hypothesis #3''': Gativus Hypothesis on the Cognitive Network and Objective Map (OMAP)]] | |||
*[[OPNT|'''Hypothesis #4''': Gativus Operating Network (OPNT)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:08, 16 December 2024
Hypothesis #2: Gativus Hypothesis on Consciousness, Mind, and Thought
Gativus hypothesizes that Consciousness, Mind, and Thought are grounded in a cognitive/knowledge network (GCON). This network is composed of:
- Knowledge Entities (KLEN), and
- Specific relations interconnecting these KLENs.
Definition and Inspiration for KLEN
The concept of KLEN is inspired by the Resource Description Framework (RDF) but extends it significantly to incorporate:
- Behavioural activity capabilities, and
- Support for multiple subjects and objects in its structure.
To describe the behavioral nature of KLENs effectively, UML activity diagrams and BPMN notation are considered the most mature and widely accepted tools. These notations align with the knowledge base of the majority of computer specialists and provide robust methodologies for modelling dynamic behaviours.
KLEN Construction and Representation
KLENs are constructed using the Gativus Network Notation (GNOT). Their design maintains associations with:
- RDF principles, and
- UML class and activity diagrams.
A detailed representation of KLEN construction within GNOT, including these associations, is illustrated below.